- Blog
- How can I become an A Level tutor?
How can I become an A Level tutor?
A Level tutoring is a rewarding and fulfilling career option for individuals who have a passion for education and a strong understanding of the subjects they wish to teach. Becoming an A Level tutor allows you to make a positive impact on the lives of students, helping them achieve their academic goals and ultimately succeed in their future endeavors. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to become an A Level tutor, covering various aspects such as understanding the A Level curriculum, requirements for becoming a tutor, key concepts and teaching strategies for A Level maths, building your expertise, marketing yourself, tips for success, online resources and platforms, and continuous professional development.

Understanding the A Level curriculum
The first step towards becoming an A Level tutor is to gain a thorough understanding of the A Level curriculum. A Levels, or Advanced Levels, are subject-based qualifications offered in the United Kingdom and other countries that follow the British education system. They are typically studied by students aged 16 to 19 and are a primary requirement for university entrance. A Levels cover a wide range of subjects, and tutors should become familiar with the curriculum of the subject they wish to teach.
To understand the A Level curriculum, tutors should research the various examination boards that offer A Level qualifications, such as AQA, OCR, and Edexcel. Each examination board has its own syllabus, assessment criteria, and resources for each subject. By studying these materials and staying up-to-date with any changes to the curriculum, tutors can ensure they are providing accurate and relevant information to their students.
Requirements for becoming an A Level tutor
Becoming an A Level tutor requires a combination of subject knowledge, teaching abilities, and professional qualities. The following are some of the main requirements for becoming an A Level tutor:
-
Subject expertise: A strong grasp of the subject matter is essential for an A Level tutor. This can be demonstrated through relevant qualifications, such as a university degree in the subject or a related field. Additionally, tutors should be prepared to continuously update their knowledge to stay current with any changes in the curriculum.
-
Teaching experience: While not always mandatory, previous teaching experience is a valuable asset for an A Level tutor. This can be gained through volunteering in schools, working as a teaching assistant, or completing a formal teacher training program.
-
Communication skills: Tutors must be able to effectively communicate complex ideas to their students in a clear and engaging manner. This includes listening to students’ needs, adapting teaching methods to suit individual learning styles, and providing constructive feedback.
-
Patience and empathy: A Level tutors should be patient and empathetic, understanding that each student learns at their own pace and may face unique challenges.
-
Organizational skills: Tutors must be able to plan and manage their time effectively, ensuring they are prepared for each tutoring session and can track student progress.
-
Professionalism: A Level tutors should maintain a professional demeanor, adhering to ethical standards and demonstrating a commitment to continuous learning and improvement.
A Level maths: Key concepts and teaching strategies
A Level maths is a popular subject for tutoring, as many students find the subject challenging and seek additional support. To become an effective tutor for maths, it is important to understand key concepts and develop effective teaching strategies.
Key concepts in A Level maths
A Level maths covers a range of topics, including pure mathematics, mechanics, and statistics. Some of the key concepts that tutors should be familiar with include:
- Algebra: manipulation of expressions, solving equations and inequalities, and understanding functions
- Calculus: differentiation, integration, and solving differential equations
- Geometry: coordinate geometry, vectors, and trigonometry
- Mechanics: motion, forces, and energy
- Statistics: probability, data analysis, and hypothesis testing
Teaching strategies for A Level maths
Effective teaching strategies for A Level maths include:
- Breaking down complex topics: Tutors should break down complex topics into smaller, manageable sections, allowing students to build their understanding step by step.
- Using real-world examples: Relating mathematical concepts to real-world situations can help students understand the relevance and practical applications of the subject.
- Encouraging active learning: Tutors should engage students in active learning techniques, such as problem-solving and critical thinking exercises, to promote deeper understanding.
- Providing clear explanations: Tutors must be able to communicate complex ideas clearly and concisely, using a variety of teaching tools and resources, such as diagrams, graphs, and interactive software.
- Adapting to individual learning styles: Tutors should tailor their teaching approach to suit the needs and preferences of individual students, ensuring that each student receives the support they require to succeed.
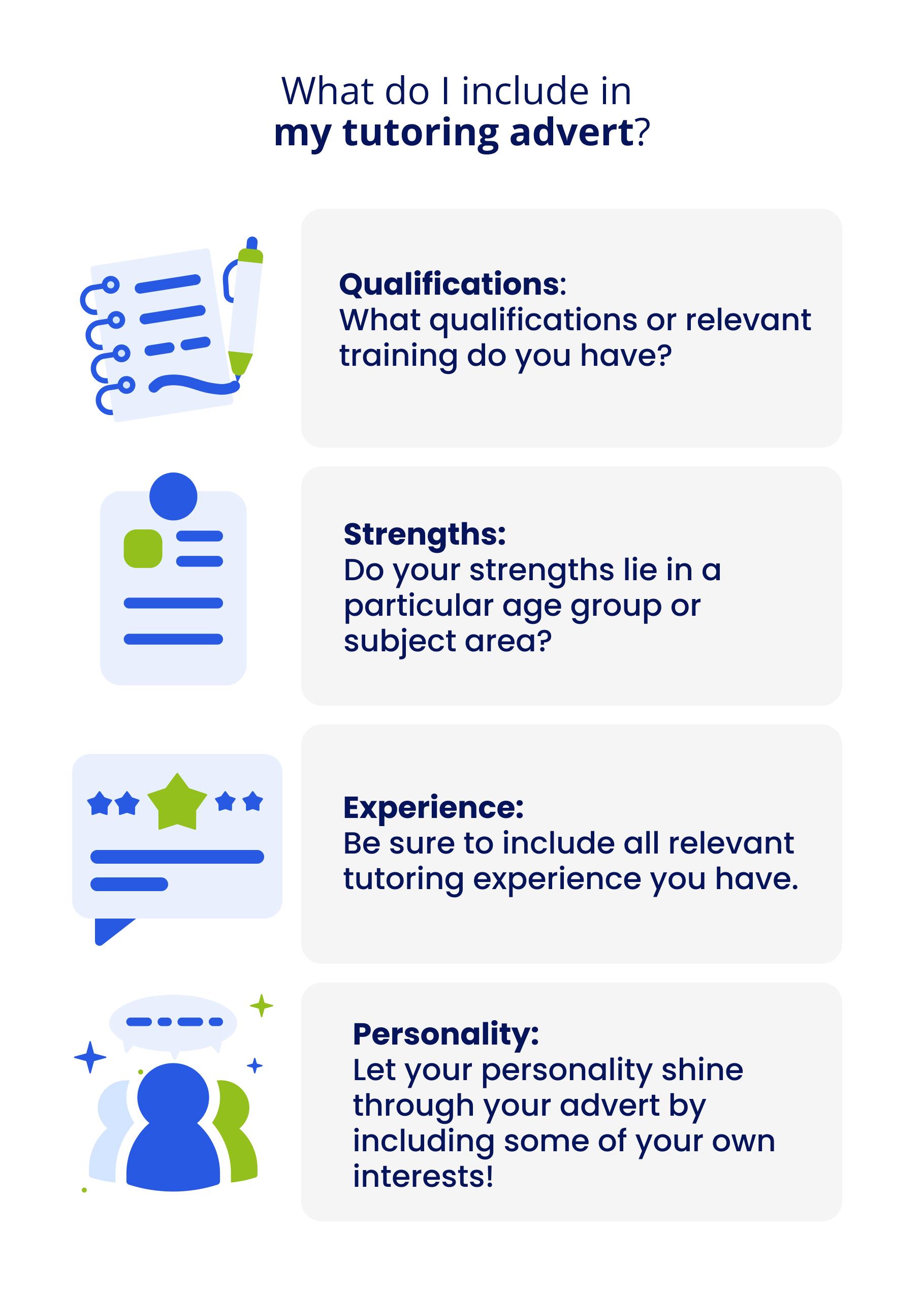
Marketing yourself as an A Level tutor
In order to build a successful tutoring business, tutors must effectively market themselves and attract potential clients. Some strategies for marketing yourself as an A Level tutor include:
-
Creating a professional online presence: Establishing a website or social media profile can help tutors showcase their qualifications, experience, and testimonials from satisfied clients. This can also provide an opportunity to share resources and insights, demonstrating expertise and commitment to the profession.
-
Networking: Building connections with local schools, colleges, and other educational institutions can help tutors raise their profile and gain referrals. Attending local events and joining relevant organizations can also provide networking opportunities.
-
Advertising and promotions: Tutors can use both online and offline advertising methods to reach potential clients, such as placing ads in local newspapers, distributing flyers, or using targeted online advertising.
-
Developing a niche: Focusing on a specific subject, age group, or learning need can help tutors differentiate themselves from competitors and appeal to a targeted market.
-
Offering incentives: Offering discounts, free trial sessions, or referral incentives can help attract new clients and encourage word-of-mouth recommendations.



